- 您现在的位置:买卖IC网 > Sheet目录287 > 24LC64XT-I/ST (Microchip Technology)IC SERIAL EEPROM 64K 2.5V 8TSSOP
24AA64/24LC64
2.0
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
3.4
Data Valid (D)
The 24XX64 supports a bi-directional 2-wire bus and
data transmission protocol. A device that sends data
onto the bus is defined as transmitter, and a device
receiving data as receiver. The bus has to be controlled
by a master device which generates the serial clock
(SCL), controls the bus access and generates the
START and STOP conditions, while the 24XX64 works
as slave. Both master and slave can operate as trans-
mitter or receiver, but the master device determines
which mode is activated.
The state of the data line represents valid data when,
after a START condition, the data line is stable for the
duration of the HIGH period of the clock signal.
The data on the line must be changed during the LOW
period of the clock signal. There is one clock pulse per
bit of data.
Each data transfer is initiated with a START condition
and terminated with a STOP condition. The number of
the data bytes transferred between the START and
STOP conditions is determined by the master device
3.0
BUS CHARACTERISTICS
and is theoretically unlimited, although only the last six-
teen will be stored when doing a write operation. When
The following bus protocol has been defined:
? Data transfer may be initiated only when the bus
an overwrite does occur it will replace data in a first-in
first-out (FIFO) fashion.
is not busy.
3.5
Acknowledge
? During data transfer, the data line must remain
stable whenever the clock line is HIGH. Changes
in the data line while the clock line is HIGH will be
interpreted as a START or STOP condition.
Each receiving device, when addressed, is obliged to
generate an acknowledge after the reception of each
byte. The master device must generate an extra clock
pulse which is associated with this Acknowledge bit.
Accordingly, the following bus conditions have been
defined (Figure 3-1).
Note:
The 24XX64 does not generate any
Acknowledge bits if an internal program-
3.1
Bus not Busy (A)
ming cycle is in progress.
Both data and clock lines remain HIGH.
The device that acknowledges, has to pull down the
SDA line during the acknowledge clock pulse in such a
3.2
Start Data Transfer (B)
way that the SDA line is stable LOW during the HIGH
period of the acknowledge related clock pulse. Of
A HIGH to LOW transition of the SDA line while the
clock (SCL) is HIGH determines a START condition. All
commands must be preceded by a START condition.
course, setup and hold times must be taken into
account. During reads, a master must signal an end of
data to the slave by not generating an Acknowledge bit
on the last byte that has been clocked out of the slave.
3.3
Stop Data Transfer (C)
In this case, the slave (24XX64) will leave the data line
A LOW to HIGH transition of the SDA line while the
clock (SCL) is HIGH determines a STOP condition. All
operations must be ended with a STOP condition.
HIGH to enable the master to generate the STOP con-
dition.
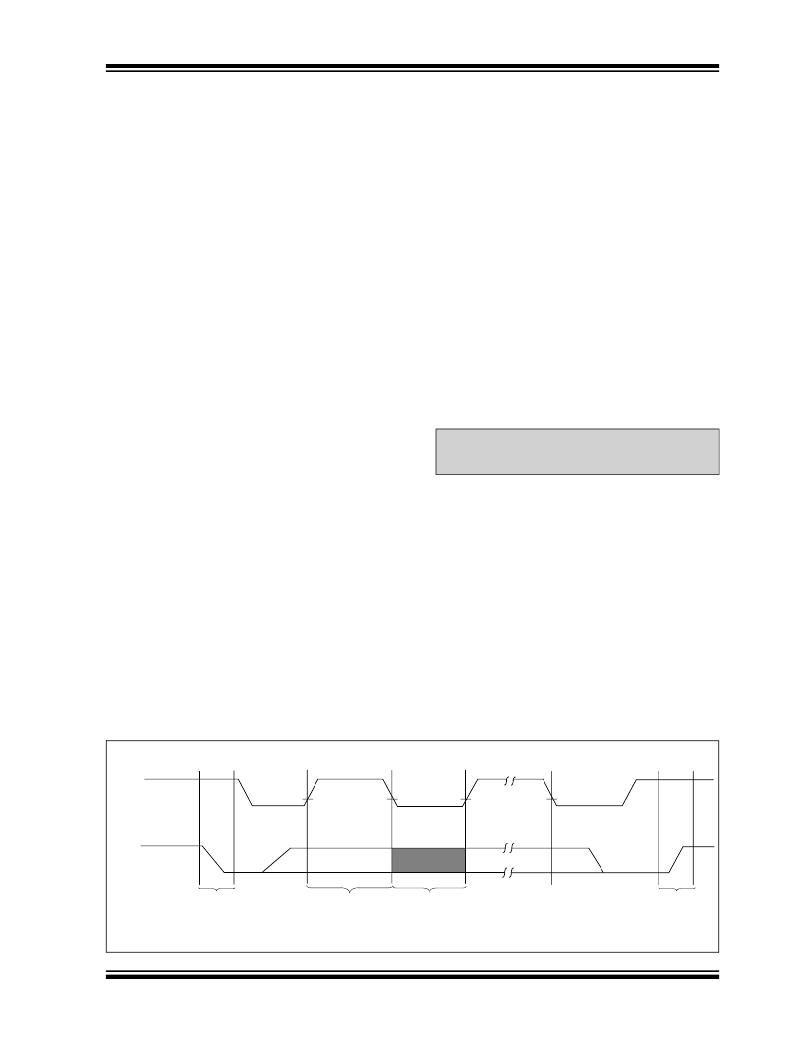
FIGURE 3-1:
DATA TRANSFER SEQUENCE ON THE SERIAL BUS
(A)
(B)
(D)
(D)
(C)
(A)
SCL
SDA
START
CONDITION
ADDRESS OR
ACKNOWLEDGE
DATA
ALLOWED
STOP
CONDITION
? 2002 Microchip Technology Inc.
VALID
TO CHANGE
DS21189F-page 5
发布紧急采购,3分钟左右您将得到回复。
相关PDF资料
24LCS21A/P
IC EEPROM 1KBIT 400KHZ 8DIP
24LCS22A-I/P
IC EEPROM 2KBIT 400KHZ 8DIP
24VL014/SN
IC EEPROM 1KBIT 400KHZ 8SOIC
24VL014H/SN
IC EEPROM 1KBIT 400KHZ 8SOIC
24VL024/SN
IC EEPROM 2KBIT 400KHZ 8SOIC
24VL024H/SN
IC EEPROM 2KBIT 400KHZ 8SOIC
25A512-I/ST
IC EEPROM 512K SPI BUS 8TSSOP
25AA020A-I/MS
IC EEPROM 2KBIT 10MHZ 8MSOP
相关代理商/技术参数
24LC65/P
功能描述:电可擦除可编程只读存储器 8kx8 2.5V Smart RoHS:否 制造商:Atmel 存储容量:2 Kbit 组织:256 B x 8 数据保留:100 yr 最大时钟频率:1000 KHz 最大工作电流:6 uA 工作电源电压:1.7 V to 5.5 V 最大工作温度:+ 85 C 安装风格:SMD/SMT 封装 / 箱体:SOIC-8
24LC65/P
制造商:Microchip Technology Inc 功能描述:IC EEPROM SMART SERIAL 64K 24LC65
24LC65/PG
功能描述:电可擦除可编程只读存储器 8kx8 - 2.5V Smart Lead Free Package
RoHS:否 制造商:Atmel 存储容量:2 Kbit 组织:256 B x 8 数据保留:100 yr 最大时钟频率:1000 KHz 最大工作电流:6 uA 工作电源电压:1.7 V to 5.5 V 最大工作温度:+ 85 C 安装风格:SMD/SMT 封装 / 箱体:SOIC-8
24LC65/SM
功能描述:电可擦除可编程只读存储器 8kx8 2.5V Smart RoHS:否 制造商:Atmel 存储容量:2 Kbit 组织:256 B x 8 数据保留:100 yr 最大时钟频率:1000 KHz 最大工作电流:6 uA 工作电源电压:1.7 V to 5.5 V 最大工作温度:+ 85 C 安装风格:SMD/SMT 封装 / 箱体:SOIC-8
24LC65/SM
制造商:Microchip Technology Inc 功能描述:IC EEPROM SMART SERIAL 64K 24LC65
24LC65/SMG
功能描述:电可擦除可编程只读存储器 8kx8 - 2.5V Smart Lead Free Package
RoHS:否 制造商:Atmel 存储容量:2 Kbit 组织:256 B x 8 数据保留:100 yr 最大时钟频率:1000 KHz 最大工作电流:6 uA 工作电源电压:1.7 V to 5.5 V 最大工作温度:+ 85 C 安装风格:SMD/SMT 封装 / 箱体:SOIC-8
24LC65-I/P
功能描述:电可擦除可编程只读存储器 8kx8 - 2.5V Smart RoHS:否 制造商:Atmel 存储容量:2 Kbit 组织:256 B x 8 数据保留:100 yr 最大时钟频率:1000 KHz 最大工作电流:6 uA 工作电源电压:1.7 V to 5.5 V 最大工作温度:+ 85 C 安装风格:SMD/SMT 封装 / 箱体:SOIC-8
24LC65-I/P
制造商:Microchip Technology Inc 功能描述:IC EEPROM SMART SERIAL 64K 24LC65